Wearables and wellbeing in buildings
In October 2018, BSRIA launched a White Paper on ‘Wearables and wellbeing in buildings - the story so far’.
The general consensus emerging from the White Paper is that, while there is substantial potential for the deployment of wearables, there are also significant technical, social and legal challenges.
It is also clear that there is little evidence of any practical solutions linking wearables to HVAC or building systems in general that are already in operation, apart from in niche areas such as wearable security fobs.
The paper looks at the kinds of wearable technologies currently available and at what needs to happen to bring viable solutions to market that link wearables and building systems in a useful way.
A wearable is taken to be an article, a device or an item of clothing which can be worn by a human, or possibly carried as an implant, which has a degree of intelligence built into it and can potentially communicate with the Internet of Things (IoT), either directly or indirectly – for example, via a Bluetooth connection to a smart phone. Animals can also wear devices or carry implants which could in some cases be relevant to building management, for example, in the case of an assistance dog or guide dog.
Examples include: smart watches, which can record various metrics of the wearer’s health and behaviour, smart glasses that can provide visual imagery, smart clothing, which can provide heating, enhanced visibility or greater sensitivity, smart hearing aids and even smart jewellery, which can, for example, issue alerts to the wearer.
Henry Lawson, BSRIA’s Senior Market Research Consultant, BSRIA’s World Market Intelligence Division said:
“At present, the practical applications of wearables are strongly focused on health and fitness, from the monitoring of basic health metrics such as exercise taken and heart rates, through to the tracking of specific and sometimes serious medical problems. There is also some overlap between health and ‘leisure’ with goals such as relaxation.
"There is growing evidence to support the common sense view that people who are healthier and happier are likely to be more productive and that this can feed into a positive financial return. There is also evidence that buildings can affect wellbeing positively or negatively both through their design and through the functionality and efficiency of the systems running to heat, cool and ventilate and light the building.
“There needs to be a means of collecting, calibrating and analysing data from a lot of different wearable devices. This immediately raises issues of consent, privacy and data security, as data relating to physical health is likely to be highly sensitive and data relating to mental states even more so. People in buildings, whether employees, customers or visitors, need a motive to share their data.
"Ironically, when it comes to emerging technology of this kind, one thing that the past has taught us is that some of the most important and far reaching applications for wearables, both inside and outside buildings, are likely to be ones that we have not even thought of yet.”
‘Wearables & wellbeing in buildings – the story so far’ White Paper published in 2018 is available (as a free copy) in combination with the purchase of additional BSRIA studies. It is a sequel to the BSRIA White Paper 'Trends towards wearables and wellbeing in buildings – a threat or opportunity for the HVAC industry?' published in 2017.
You can access the report at: https://www.bsria.co.uk/accounts/register/?file=wp8-2018-wearables-and-wellbeing-in-buildings.pdf
This article was originally published here by BSRIA on 18 October 2018.
--BSRIA
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
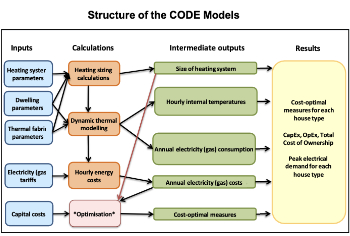
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.